| POTASSIUM HYDROGEN OXALATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 127-95-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 204-873-0 | |
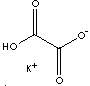
| FORMULA | C2HKO4 | |
| MOL WT. | 128.13 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2917.11.0000 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Potassium acid oxalate; Potassium binoxalate; | |
| Ethanedioic acid monopotassium salt; Kleesalz; Monopotassium oxalate; Oxalic acid monopotassium salt; Potassium hydrogen oxalate; Potassium quadroxalate; Potassium salt of sorrel; Sal Acetosella; Salt of sorrel; Sorrel salt; Potassium 2-hydroxy-2-oxoacetate; | ||
| SMILES | C(C(=O)[O-])(O)=O.[K+] | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Oxalate, Chelating agent | |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystals | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 2.5 g/100g | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| log P | -4.98 (Octanol-water) | |
| OH RATE CONSTANT | 5.20E-13 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric ) | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
|
PubChem Compound Summary - Potassium binoxalate http://scripts.iucr.org/ Local: |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystals | |
| PURITY | 99.0% min | |
|
CHLORIDE |
0.01% max | |
|
SULFATE |
0.01% max | |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max | |
|
IRON |
10ppm max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 2811 | |
| PRICE INFORMATION | ||
|
|
||